10 Business Studies 4
Section outline
-
Kia Ora and a very warm welcome everyone to Business Studies!
I am thrilled to have you all on board and look forward to working with you on all our challenges/tasks and projects.I am sure we will have a great time.
During our first week of meeting (in Week 2) we are going to get to know each other better and look at the course expectations.
Our learning outcome for this week is to be able to understand the outline for Business for this term.
Enjoy the first week back and remember to keep an open mind about new ideas (think outside the box).
CONTENTS
- Team building
- Entrepreneurs
- Types of Business
- Markets & segmentation
- Market Research
- Marketing Mix - Product, Price, Place, Promotion
- NCEA 1.4 Marketing Mix
- The role of markets - houses, shares, commodities
- Economics
- Business Issues, goals and stakeholders
- Finance & Accounting
- Market Day - putting it all together
- Web text - Wikibooks GCSE Business Studies
-
Kia Ora Everyone
As we missed one session due to the public holiday, the focus this week is on Getting to know each other and introducing you to the outline for the Business Studies Option.
Team Building
Learning Intentions- Start to 'Form' our class as a team
- Build relationships (learn names, backgrounds, etc)
- Discover our Business 'prior knowledge'
- We have worked together to complete a task
- We found things that we have in common
- We know the meaning of common business terms
Activities:- Contribute to the shared Google Doc in Google Classroom called 'BUSINESS STUDIES INTRODUCTION"
- The doc asks you to add a photo of something that represents who you are as a person (eg you might be adventurous, home loving, or sporty).
- It asks you to give some information about yourself (a strength or skill that you're proud of, why you chose Business Studies, an embarrassing moment, etc.).
- The doc also presents some skills that you may have or need to develop.
- Think about what stage our class team is at - here's a simple resource on 'Stages of Team Formation'
- Please join the Google classroom page: Class code: yw6zous
- Start to 'Form' our class as a team
-
Kia Ora Everyone
This week we will be focusing on Entrepreneurs by looking at their skills set and how you can apply these skills in a Business Studies setting.
Learning Intentions- Study case studies of entrepreneurial people
- Investigate the nature of entrepreneurs.
- Explore business purpose/goals/types/examples
- Research pros & cons of business activities (eg multi-national, limited liability)
- We can define an entrepreneur and describe the attributes of an entrepreneur
- We can identify people with entrepreneurial attributes and name examples of entrepreneurial people
- We have identified our own entrepreneurial strengths and areas to develop
- We can explain the nature of business and its pros & cons.
Do Now - Entrepreneurs- DO NOW - Read article below
- Exploring the CNBC "Make it" and Inspiring stories NZ website
Notes
An entrepreneur has an idea and risks time, money and reputation putting the idea into action as a business.- https://www.businessnewsdaily.com/2642-entrepreneurship.html (Please read this article for homework)
Entrepreneurs are innovative. They:
- Have ideas AND can put them into action
- Are creative problem solvers (think outside the box)
- Work long hours
- Can sell and / or build
- Can simplify processes and data - identify what's important
- Are effective with people
-
Kia Ora Everyone
This week we will continue focusing on Entrepreneurs by looking at their skills set and how you can apply these skills in a Business Studies setting.
Learning Intentions- Study case studies of entrepreneurial people
- Investigate the nature of entrepreneurs.
- Explore business purpose/goals/types/examples
- We can define an entrepreneur and describe the attributes of an entrepreneur
- We can identify people with entrepreneurial attributes and name examples of entrepreneurial people
- We have identified our own entrepreneurial strengths and areas to develop
Do Now - Entrepreneurs- DO NOW - Business Quiz (CETA)
- Share homework: Scenario - Market day skills
- Exploring the Inspiring stories NZ website
Notes- https://www.businessnewsdaily.com/2642-entrepreneurship.html (Please read this article for homework if you have not finished this in class)
Entrepreneurs are innovative. They:
- Have ideas AND can put them into action
- Are creative problem solvers (think outside the box)
- Work long hours
- Can sell and / or build
- Can simplify processes and data - identify what's important
- Are effective with people
Whole Class Activity- As a whole class, we'll watch the video "Caine's Arcade Part 1"
- Each small group choose a different attribute from the list of 6 above
- Create and share with me a Doc called "Entrepreneurs- Caine's arcade", type things that Caine says or does that shows that he has your chosen attribute?
Small Group Activity- As a whole class, we'll watch the video "Stupid ideas - Dragon's Den"
- In your small group, discuss whether you think Rupert Evans is an entrepreneur and which of the 6 attributes is he the weakest.
Homework- Watch the video Caine’s Arcade Part 2.
- In groups share whether you think Nirvan Mullick (Caine’s first customer) is an entrepreneur and explain why.
Extra Case Study- Research some "Entrepreneurs", those who are proclaimed "Youtube millionaires". Read up on them and discuss as a group if these people are entrepreneurs.
- If you had a chance to do something likewise, what could your Youtube channel focus on? Create an google doc called" Entrepreneurs - You tube sensation" to write your answers.
- You and your group will then present/pitch your idea to the class by Week 5.
-
Kia Ora Everyone
This week we will continue focusing on Entrepreneur skills and application of these skills in a Business Studies setting.
Learning Intentions- Study You Tube videos of entrepreneurial people
- We can display Entrepreneurship skills (creativity, innovation, communication skills) by presenting our You Tube ideas
Activities:- Continue working on your You Tube slideshows
- Pitching your You tube idea to the class.
Resources to support your pitch:
https://youtu.be/QLUyzXhoBik
https://youtu.be/bbQcEWYPbqs
https://youtu.be/pjKbagr2Bvg
-
Kia Ora Everyone
This week we will be focusing on the different types of Business structures
Learning Intentions
- We are understanding the different business structures
- We can explain the structure of business and its pros & cons
- We explored various examples of the business structure and understand the comparisons
Activities:- Identify various business that fall under the Business structures that you have studied. Look up Business that you are are familiar with and identify what Business structure they fall under.
-
Kia Ora Everyone
Learning Intentions
- We are understanding the foundations of Business
- We have developed knowledge on Business basics and it's tools by exploring the MBIE & Business.govt sites
Activities:- Navigating through the Business websites
- After exploring the websites, answer the questions on Google classroom
-
This week the focus is on Team Building and the importance of working collaboratively in team.
- Consider how to build a team (not just a group)
- Understand that diversity in a team is a strength
Success Criteria:
- Working collaboratively in a team leads to a successful product or outcome
- Working in team is an important skill in forming a Social Enterprise/ Business
Activities:
- Team Activity:
- Participation in Team Challenge 2 (Choose roles in a group according to your self assessment tool task in Week 1)
-
This week the focus is on Team Building and skill development.
- Consider how to build a team (not just a group)
- Understand that diversity in a team is a strength
Success Criteria:
- Working collaboratively in a team leads to a successful product or outcome
- Working in team is an important skill in forming a Social Enterprise/ Business
Activities:
- Production focus group
- Production ideas and brainstorm
-
Markets & Segmentation
Learning Intentions- Study case studies of markets and marketing
- Investigate the nature of marketing: Plan, Strategy and Segmentation.
- We can define and explain Markets
- We can describe how & why markets are segmented
- We have added to the glossary of business terms
Markets- A Market is a way in which buyers and sellers exchange goods or services. It can be a physical marketplace like a bazaar or shopping centre, or a virtual, online market (eg share or money market, Trade Me, eBay). Resource on markets
- Maeklong Market in Thailand has hundreds of small vendors using identical stands with identical shade awnings, selling identical products. Many sell the same types of fresh fish, others the same types of vegetables, and others the same cooked food.
ACTIVITIES:
Market Segments

A Market Segment is a group of individuals with similar characteristics, eg Generation Z, retired couples, teenage girls, DINKYS.
For example, markets can be segmented by gender, age & life-cycle stage, socio-economics, ethnicity, lifestyle / family type, location, product use.
By segmenting the market, businesses can more accurately meet the needs of their target market. They can offer variations of their product that make the consumer think one variation is specifically designed for them and so they are willing to pay a higher price.
- Study case studies of markets and marketing
-
Kia Ora Everyone
Marketing & Market Segmentation
Success Criteria
Learning Intentions- Explore the process of marketing in a business
- Investigate the process of market segmentation in identifying the target market for specific products or services
- We can define marketing and market segmentation
- We can identify the basic market segments: demographics; psychographic; geographic; behavioural
- We are able to identify the characteristics of each market segment
- We are able to describe the target market for specific products or services
Marketing follows a market oriented approach where businesses seek to identify customer wants, and future wants and then goes about trying to satisfy them profitably.
To do this they must first determine who the most likely users or consumers of their products or services are. This will allow them to identify the needs and wants of these consumers to ensure that their product is developed to meet these needs. The group identified is called the target market.
Market SegmentationTo help identify the target market, prospective customers are divided into groups (segments) that have common needs and wants. There are many ways to do this. Four common segments used by marketers are:
Possible Target Market for Ferrari F8 Tributo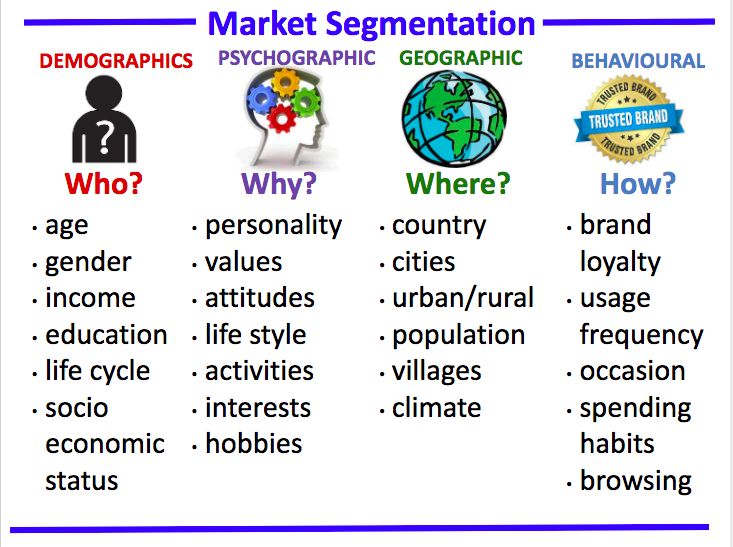
Demographic
Age: Middle aged. This because the are most likely finished university etc and have been working for some time to accumulate enough wealth to purchase this car
Gender: Most likely male.
Socio Economic Status: High income.
Family life cycle: Single or retired, Children have grown up. Car is a two-door, so is not suitable for passengers apart from the owners partner or date.
Psychographic
Sporty. Likes car racing, speed etc. Possibly F1 fan as Ferrari races in F1.
Social status: Wealthy to be able to afford this car.
Personality: Wants people to know his social status, know that he is successful (rich).
Values & Attitudes: Wants something exclusive that not many other people have.
Geographic
Resides in a wealthy suburb
Large cities in well developed countries
Behavioural
Likes luxury. Happy to spend for high quality. Brand must be well known.
TASK: Using all four of the basic market segments above, identify the possible target market for the products below. Explain your answer by stating reasons for your suggestions.
Dove beauty soap
Barbie Doll
Revlon Lipstick
Toothpaste is toothpaste, right? Wrong - at least, not in the Marketing Department. In small groups, discuss the different types of toothpaste available in the shops. This Countdown online shopping site might help. Find other products where the market has been segmented.
-
Kia Ora Everyone
Marketing & Market Segmentation
Success Criteria
Learning Intentions- Explore the process of marketing in a business
- Investigate the process of market segmentation in identifying the target market for specific products or services
- We can define marketing and market segmentation
- We can identify the basic market segments: demographics; psychographic; geographic; behavioural
- We are able to identify the characteristics of each market segment
- We are able to describe the target market for specific products or services
Marketing follows a market oriented approach where businesses seek to identify customer wants, and future wants and then goes about trying to satisfy them profitably.
To do this they must first determine who the most likely users or consumers of their products or services are. This will allow them to identify the needs and wants of these consumers to ensure that their product is developed to meet these needs. The group identified is called the target market.
Market SegmentationTo help identify the target market, prospective customers are divided into groups (segments) that have common needs and wants. There are many ways to do this. Four common segments used by marketers are:
Possible Target Market for Ferrari F8 Tributo
Demographic
Age: Middle aged. This because the are most likely finished university etc and have been working for some time to accumulate enough wealth to purchase this car
Gender: Most likely male.
Socio Economic Status: High income.
Family life cycle: Single or retired, Children have grown up. Car is a two-door, so is not suitable for passengers apart from the owners partner or date.
Psychographic
Sporty. Likes car racing, speed etc. Possibly F1 fan as Ferrari races in F1.
Social status: Wealthy to be able to afford this car.
Personality: Wants people to know his social status, know that he is successful (rich).
Values & Attitudes: Wants something exclusive that not many other people have.
Geographic
Resides in a wealthy suburb
Large cities in well developed countries
Behavioural
Likes luxury. Happy to spend for high quality. Brand must be well known.
TASK: Using all four of the basic market segments above, identify the possible target market for the products below. Explain your answer by stating reasons for your suggestions.
Dove beauty soap
Barbie Doll
Revlon Lipstick
-
Marketing Mix
Learning Intentions
- Investigate the meaning and relevance of the Marketing Mix (4 Ps)
- Explore the 'Product' element of the Mix, through case studies and examples
- Can explain the meaning and relevance, with examples, of the Marketing Mix 4 Ps
- Can explain and apply understanding of the Product element of the Mix.
Marketing is the process of gathering information about people in the market and then acting on that information to influence their beliefs or decisions about your products or business.
The Marketing Mix contains the variables that can be changed in order to influence people's beliefs or decisions. In business, the aim is usually to attract customers to buy the product (to satisfy their needs or wants). These variables are called the 4Ps:- Product design features, quality, packaging, after-sales service, etc
- Price skimming, penetration, etc
- Place distribution channels, delivery, retail outlet, mail order, etc
- Promotion advertising, sales promotion, personal selling, publicity, etc
Task 1
Introduction to marketing - Bottled water (Task on google classroom)
Task 2
In small groups, discuss the 4Ps of these businesses or products:- Local Dairy shop
- Pack'n'Save supermarket vs Farro supermarket
- Apple computers and phones
- Nike shoes
- Homebrand product range (at Countdown supermarket)
-
Learning Intentions

Learning Intentions
- Investigate the purposes of promotion and how businesses promote themselves and their products.
- Explore examples of different promotion methods and what makes them successful.
- Can describe several ways to promote products and the aim of each one.
- Can analyse examples of promotions.
Promotion
Promotion is a range of techniques for communicating with the 'external environment', especially customers. These techniques include:
- Advertising is any communication paid for by the sender and intended to inform, influence or persuade the receiver.
- Personal selling any person to person communication designed to inform potential customers or to persuade them to buy.
- Sales promotion is any financial or economic incentive to encourage a customer to buy.
- Publicity also known as public relations, is communication free of charge which is either within, or out of, the sender's control.
Promotion objectives
The objectives of promotion are summarised by A.I.D.A.:
- Awareness To get people to know that your product exists
- Interest To get people to be interested in what your product might do for them
- Desire To make people want to have your product
- Action To get people to actually spend money buying your product

The purpose of each promotion technique

Advertising is better at telling people that `your product exists and making them interested to find out more. An advert on the TV, say, is unlikely to make a person jump in the car go to the shop and pay money to buy your product.
A sales promotion, such as "buy a Nissan Leaf car in July and we'll give you free insurance for two years" might get people to decide that your car is the one they want. It might perhaps encourage them into the shop, but it is the salesperson who will finally actually convince them to pay money.
Examples of promotions - discuss whether each promotion will achieve Awareness

-
Promotion continued
Another consideration when planning promotion is whether the business is trying to get new customers to try the product for the first time or whether they are trying to get existing customers to keep buying the product. Try answering these 3 multiple choice questions:
1. A publishing company is about to launch a new magazine aimed at female readers aged 14-20. Which two of the following would be direct ways in which the company could try to get potential readers to buy the first issue of the magazine? (Select two answers).
- A) Keep production costs low
- B) Offer a free lipstick with the issue
- C) Take on extra staff
- D) Sell the first issue at half price
- E) Cut advertising on the other magazines by the company
2. A car manufacturing company is worried that there is little customer loyalty amongst car buyers for its vehicles. The lack of customer loyalty is most likely to mean that (select one answer):- A) customers are buying a different make of car when they sell their existing car
- B) car sales for the company are increasing
- C) the cars the company sells are seen as being good value
- D) it would be more profitable for the company to make large cuts in the price of its cars
3. A company making frozen pizzas depends for its success on repeat purchases. Customers are most likely to make repeat purchases because (select one answer):- A) it determines the amount of profit the company makes
- B) it increases sales of pizzas
- C) the company spends heavily on advertising
- D) in the pizza market, customers have little brand loyalty
Questions to check understanding
Here are links to some multiple choice questions. See if your small group can answer them:
- https://www.tutor2u.net/business/quiz/marketingmix20/quiz.html
- https://www.bbc.com/education/topics/z96pyrd
Resources
Digital MarketingP&G - the world's largest marketer slide show
https://www.slideshare.net/HarshitGupta245/harvard-case-study-analysis-pg -
Learning Intentions
- Investigate the meaning and relevance of the Marketing Mix (4 Ps)
- Explore the 'Product' element of the Mix, through case studies and examples
- Can explain the meaning and relevance, with examples, of the Marketing Mix 4 Ps
- Can explain and apply understanding of the Product element of the Mix.
Product
A product is a good (tangible) or a service (intangible) produced by an organisation. Companies can grow using existing or new products:
 Strategies for each method of growth
Strategies for each method of growthMarket penetration: encourage consumers to use more, 'steal' competitor's customers
Market Development: new uses for products, new markets geographically, new segments
Product development: modify existing products (eg new shapes), upgraded model, 'me-too' copycat product
Diversification: risky as you have less knowledge & experience (may buy an existing business).

Discussion: In small groups, discuss whether the cartoon above about fire fits the definition of diversification in the table.
Activity: In Google Classroom, complete the Google Doc called 'Marketing Mix - Product'.Value Analysis
 Value analysis is the process of deciding which product features most attract or satisfy a target customer's needs.For example,
Value analysis is the process of deciding which product features most attract or satisfy a target customer's needs.For example,- Function will be most important when buying a parachute!
- Fashion clothes or bought mostly on the basis of aesthetics (how they look).
- Economic manufacture is important for customers who have low income.
Activity: In the Google Doc called 'Marketing Mix - Product', answer the questions on Product Life Cycle.
Product Life Cycle
 Sales, costs and profit of a product follow a series of stages over its life.
Sales, costs and profit of a product follow a series of stages over its life. When being developed, there are no sales, high costs and no profit - just losses.
A newly introduced product has slowly growing sales, high costs & no profit.
Sales increase rapidly during the Growth stage, unit costs start to fall and some profit may be made.
As competitors enter the market during Maturity, sales stop growing, costs reduce and profits are high.
When the market becomes saturated with too many businesses competing for customers, a price war can start and some businesses drop out. Costs remain constant, but sales and profits decrease.
The market declines and the product eventually becomes unprofitable.

Discussion: In small groups, discuss the range of life cycle diagrams on the right and think of examples of real products for each one.
Activity: In the Google Doc called 'Marketing Mix - Product', answer the questions on Product Life Cycle.The life cycle is important because:
- each stage needs a different marketing mix
- a business needs products at different life stages to survive long term.
Businesses try to extend products' lives beyond the saturation stage and so might repackage or slightly change it. Lux soap is more than 100 years old and its shape, perfume, colour, size and packaging have all changed to maintain consumer interest in it. Other extension strategies are finding new uses or accessories for the product. Examples of long lived products are Dettol, Bisto, Persil, Marmite, Coleman's mustard, Tetley tea. Extension strategies
Extension strategiesLife cycles are getting shorter as technological change accelerates. Products can become obsolete within months as more advanced versions are released.
Product portfolio

It helps to sustain your business to have a range of products at different stages of their life cycles, so that as sales of one decline, sales of others are growing.
In the product portfolio, some products may be cash cows, which are established brands in mature markets. The main work has been done. They sell well, bring money in, but are unlikely to increase sales. Every business wants these!
Stars are also great to have because, not only are they strong brands in the market, but also the market is growing and so income and profits will probably increase.
Dogs are products that are sold to the last, loyal, 'die hard' customers. They are not attracting new consumers and will probably be phased out.
Question marks are in a growing market and may become established, popular brands, but this is uncertain. Work is needed here to make them stars.
Obsolescence
 Obsolescence is the process by which products become divided, discarded or 'overtaken' by more up-to-date versions or products (eg vinyl records, magnetic cassette-tapes, CDs, MP3 players).
Obsolescence is the process by which products become divided, discarded or 'overtaken' by more up-to-date versions or products (eg vinyl records, magnetic cassette-tapes, CDs, MP3 players).
Built-in obsolescence results from the product's design or durability (ie how long before it wears out).
Planned obsolescence is making a product out of date by deliberately introducing a new version or product.
Discuss examples of products that became obsolete without their manufacturer's intention.
Discuss examples of products that are obsolete because their manufacturer deliberately released a new product.Discuss why obsolescence might benefit a company (eg Apple iPhones)
-
Learning Intentions

- Explore product differentiation & branding (part of the Product element of the 4Ps).
- Focus an analysis of a product or business by using a SWOT analysis.
- Can explain the purpose of branding (including logos and slogans) and identify popular examples.
- Can perform a SWOT analysis to analyse a product or business.
- Can describe 4 reasons for packaging and analyse a product's packaging.
Product differentiation and Branding
Businesses often use slogans, for example "The Warehouse, where every one gets a bargain" and "Briscoes, you'll never buy better".
 They also use logos These marketing tools are designed to be memorable and businesses spend a lot of time and money associating them with certain values and emotions in customers. They are a large component of the brand'.
They also use logos These marketing tools are designed to be memorable and businesses spend a lot of time and money associating them with certain values and emotions in customers. They are a large component of the brand'.A brand is any name, term, symbol or distinctive packaging that identifies specific goods or services and helps to differentiate them. With legal protection, it becomes a trademark. Brands can be linked to businesses, single and family line products. Branding helps to achieve marketing objectives by:
- being a focal point for advertisng
- encouraging repeat purchase (customer loyalty)
- allowing non-price competition (product differentiation)
- making it easier to expand a product range
- making it cheaper to advertise (the whole brand rather than every individual product)
Branding can hep customers by:- making it quicker to identify 'good' and 'bad' products
- identifying the business behind the product
- encouraging the business to provide consistent quality
Single product line and Multiple product line
Some businesses produce just one product and advertise its brand eg WD40 spray and Crocs shoes. Others produce a wide range of different products and advertise both each one but also the business's brand eg Kelloggs make a wide range of food products, but the name Kelloggs is prominent on packaging and in advertising.
Here's a great online article on this topic
Packaging
There are 4 reasons for packaging:
- Ease of carrying and protection eg liquids, fragile or dangerous goods, powders
- As part of the Marketing Mix - it can contain the trademark or logo, be eye-catching or distinctive. New packaging can be a cheap way to give the impression that the product has been changed or improved.
- To enhance apparent value to the customer and thus enable higher prices and profits eg perfume, Ferrero Roche chocolates
- Makes stock taking easier - especially in self service stores where theft or damage may be issues.
Product oriented vs Market oriented
A business that is product orientated has a dominant production or research & development department that creates a product and then relies on the marketing department to find a market for it. A market orientated business has a dominant marketing department that identifies trends and needs and then asks the production department to create products that meet that need.As a class, we'll listen to Lucy Kellaway's radio clip on the internet of things and new product development, entitled 'We need smart products because we're stupid'. Given that she believes no-one actually needs "a fridge that tells you when you need more milk", consider whether the internet of things is a market or product oriented development. - Explore product differentiation & branding (part of the Product element of the 4Ps).
-
Learning Intentions

- Investigate ways in which businesses distribute their products to customers.
- Explore examples of different distribution channels and what affects business's choice of channel.
- Can describe several ways to distribute products and the factors that affect this choice.
- Can provide examples of different distribution channels.
Place
Distribution (Place) ensures products are available to customers in the right quantity at the right time in the right place. It involves questions like:
- Where do consumers prefer to buy the product?
- How can we ensure the product is available to existing and potential customers?
- How important are speed, timing, cost, availability
- How much stock should we hold? Too little and we run out; too much and we tie up cash (that then cannot be used to pay daily expenses)
It depends on:- The product - is it perishable, technically complex, a convenience item?
- The market - is it geographically spread out, highly competitive?
- The business - is It large, supplying producers or consumers?
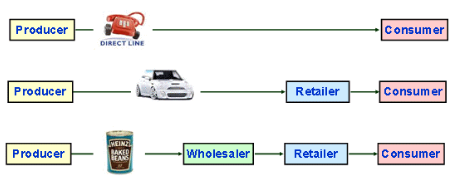 A distribution channel is the means by which the product moves from production to consumption. It might include:
A distribution channel is the means by which the product moves from production to consumption. It might include:- Retailer sells direct to households / end users / consumers
- Wholesaler sells products from different manufacturers to retailers; they 'break bulk' by putting large quantities into smaller packages
- Distributor have a contract to sell a manufacturer's products
- Agent a 'go-between' who never owns the product and earns commission eg real estate, insurance, travel.
- Franchisee allowed to trade under the the manufacturer's name; pays a fee and gives a share of the revenue to the franchisor
- Direct selling door to door, mail order, sales reps
Trends in distribution are:

- more out of town stores and malls (in Europe, malls are closing);
- fewer independent and more multiple / chain retailers;
- more franchises (eg Jim's mowing);
- online shopping and home delivery.
- drone and driverless delivery??
NZ's supermarket duopoly
Read the following article. Note which companies own Pak'n'Save, New World, Countdown. In your group, discuss how it affects you and your family that two companies dominate the NZ supermarket industry.
NZ Herald: Big two supermarket chains locked in fierce food fight
In your group, find out the meaning of 'parallel imports' and discuss why they might be cheaper to buy and whether there are any disadvantages.Extension activities
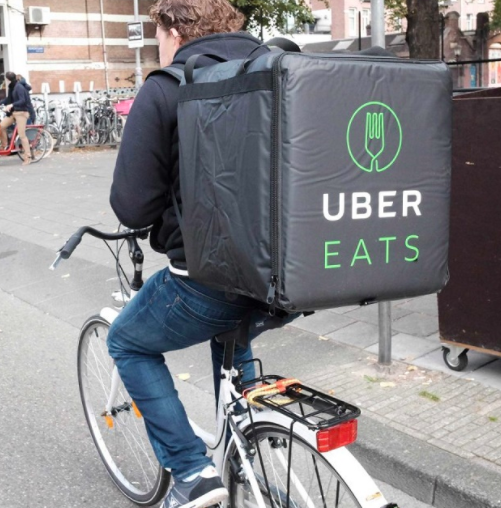 Research the service that Uber Eats provides.
Research the service that Uber Eats provides.
Consider the impact on distribution of restaurant food.
How do restaurants and householders benefit?
Watch this video clip on drone delivery and discuss the impact on distribution channels and on different organisations that might be affected.
Watch this video clip on 3D printing and and discuss the impact on distribution channels and on different organisations that might be affected. -
Learning Intentions

- Investigate ways in which businesses can price their products
- Explore examples of different pricing strategies and reasons for using each strategy.
- Explore the specific effect of changes in price on quantity sold and thus on profit.
- Can describe several key strategies for pricing products
- Can predict the effect of a price change on sales and thus profits.
Price
The price of o product sends strong messages to consumers. Would you buy a parachute in a sale at half price, or a perfume, for a valued friend, that was advertised as being low price, or petrol at a much higher price than competitors' prices?
Pricing strategies
- Cost-plus pricing - adding a percentage markup to the estimated unit cost.
- Penetration pricing - initial low price to encourage customers to try the product (but could send the message of low quality).
- Skimming - high price until competition forces it down
- Competitive pricing - in line with, or a certain percentage above, competitors' prices.
- Psychological pricing - appears closer to customer's perceived value (eg $3.99)
- Prestige price - to promote a luxury image (eg perfume)
- Price discrimination - price for the same product varies for different customer groups (eg students, off-peak travel).
- Loss leader - very low price attracts customers into the shop to buy other products at 'normal' prices.
- Promotional pricing - low price for a short time to renew customer interest or clear unwanted stock.
- Range pricing - prices of similar types of product kept within limits.
In your group, discuss which price strategy is being used in each of the examples below:
- A watch that’s very similar to others sold in the shops
- A toy sold for $1.95
- A tour operator sells holidays during the school holidays as well as at other times.
- A new brand of washing powder is launched - there are several similar ones already available
- A supermarket wants to cover the cost of vegetables and make a 100% profit as well.
- A new mobile phone has been developed that has extra features compared to the competition.
-
Learning Intentions

- To reflect on our understanding of Marketing topics and to prepare questions for the guest Marketing Executive from Krispy Kreme.
- To prepare for the issuing of the NCEA assessment (brainstorming products to choose from and evaluating exemplar answers).
- Can identify Marketing concepts that are not fully understood and discuss these with a Marketing Professional who is working in the field.
- Can describe the requirements of the NCEA assessment and have identified a small number of potential products and research sources.
Dove - a Marketing case study
In Google Classroom is a slide presentation case study of the marketing of Dove products. Study the presentation slides and write a question on a post-it note for the class to help revise marketing.
Antonio Rivera, Operations Manager
(Rebecca Woodley, Marketing Executive)
In week 9, Antonio Rivera is visiting us at school. Antonio is in charge of Krispy Kreme's Marketing in New Zealand. He has kindly agreed to share elements of Krispy Kreme's marketing strategy, and details of their Marketing Mix. This is very relevant to your NCEA assessment.
-
Learning Intentions

- To apply what we've learned in class to a real life product
- To experience an NCEA Level 1 assessment (and hopefully gain 3 credits at Excellence)
- Understand the importance of SEXY paragraphs and can write these.
- Have entered in the GDoc which product's Marketing Mix I'm analysing.
- Have read the student instructions and mindmapped my draft report.
- Understand what I need to do for Achieved, Merit & Excellence grades (using the examples of student work)
- Have started the draft final report and completed 1 of the 4 P'
-
Learning Intentions
- To apply what we've learned in class to a real life product
- To experience an NCEA Level 1 assessment (and hopefully gain 3 credits at Excellence)
- To follow and complete the MHJC assessment using the set criteria
- Understand the importance of structured writing using (SEXY/PEDAL/PEEL/TEXAS paragraphs) and can write these.
- Have applied the marketing mix to my chosen product
- Have read the student instructions and mind-mapped my draft report.
- Understand what I need to do for Achieved, Merit & Excellence grades
- Have started the draft final report
Activities:
- Checkpoint 1: Research file completed (by 24 July 2022)
- Checkpoint 2: Draft report using information from the research file (End of Week 1- T3)
- Checkpoint 3: Final report to submit by the due date: 5 August 2022 (End of Week 2- T3)
-
Learning Intentions
- To apply what we've learned in class to a real life product
- To experience an NCEA Level 1 assessment (and hopefully gain 3 credits at Excellence)
- To follow and complete the MHJC assessment using the set criteria
- Understand the importance of structured writing using (SEXY/PEDAL/PEEL/TEXAS paragraphs) and can write these.
- Have applied the marketing mix to my chosen product
- Have read the student instructions and mind-mapped my draft report.
- Understand what I need to do for Achieved, Merit & Excellence grades
- Have started the draft final report
Activities:
- Checkpoint 3: Final report to submit by the due date: 5 August 2022 (End of Week 2- T3)
Uploading information:
- Please ensure that you upload the following
- Research template
- Report
- Upload by 5 August at 4pm
-
Learning Intentions
- To apply what we've learned in class to a real life product
- To experience an NCEA Level 1 assessment (and hopefully gain 3 credits at Excellence)
- To follow and complete the MHJC assessment using the set criteria
- Understand the importance of structured writing using (SEXY/PEDAL/PEEL/TEXAS paragraphs) and can write these.
- Have applied the marketing mix to my chosen product
- Have read the student instructions and mind-mapped my draft report.
- Understand what I need to do for Achieved, Merit & Excellence grades
- Have started the draft final report
Activities:
Uploading information:
- Please ensure that you upload the following
- Research template
- Report
- Upload by 12 August at 4pm
-

Kia ora Everyone
Please note that Market Day takes place in Term 4: Week 2. Please diarise this date: 1 November
AO: Understand how exploration and innovation create opportunities and challenges for people, places, and environments.
Learning Intentions: We are learning to (WALT)...
Explore a range of advertisements from local newspapers, videos etc to gain an understanding of what is a market place.
Understand the different types of markets.
Understand the terms consumers and producers and determine what is their role involves in the market place.
Understand what is target audience
Success Criteria: I can/have...
Understand the different types of markets.
Developed extensive knowledge of core key terms that would assist my understanding of market day.
Understand the role local markets plays in our community.
Define and describe what is a target audience
Activities:
1. Define: Street market and famers market
2. Vocab box : Distribution, Markets, Buyers (Consumers), Sellers, Prices, Goods and Services, Sales Revenue, Costs, Profits, Marketing, Transaction, Consumer Rights, etc
3. Group formation and Brainstorm ideas for Market day
4. Assessment 2: Introducing the assessment
-
Kia ora class,
My name is Ms Al-Chalabi and I am a student teacher from Massey University. By now you have met me and know that I will be training with Mrs Selagan until the end of this term. I will be teaching you most of the sessions from now until the end of the term and I am looking forward to this exciting journey with you.
This week our focus is on Market research, and we will be working in the spirit of the following Maori whakatāuki (proverb):He aha te mea nui o te ao?
What is the most important thing in the world?He tāngata, he tāngata, he tāngata.
We are reminded that in business we are constantly trying to satisfy our target market needs, we care about our people (customers) and that is why we want to find out more about who they are and what they need and want.
It's people, people, people.Learning Intentions
- Recognise the importance of market research for a business and how to conduct a market research for a new or existing product.
- Interpret market research data.
Success Criteria
- Conduct Market research for products planned for the upcoming market day.
- Analyse data collected from market research.
-
Kia ora class,
This week we start our focus for the remainder of the term - Business Planning. Throughout this module we will be guided by a Māori concept of planning for achievement. The following whakatāuki
speaks to the importance of having a ‘plan of attack’; it could be used to guide conversation or lead a discussion in the planning of an event or community initiative (or a small business).
"Tē tōia, tē haumatia" Nothing can be achieved without a plan, workforce and a way of doing things.
Learning Intentions/ Mo te ako
- Apply product costing formula.
- Calculate Market Day product prices.
- Understand the importance of business planning and business objectives.
Success Criteria
- Apply product pricing formula to determine product prices.
- Produce a list of retail price for Market Day products.
- Write smart objectives for planning for a the small business you have already created to participate in the market day.
Learning Activities
Note: All the activities are set up on your Google Classroom.
Monday 29 August
- Do now starter activity - finalise working on your surveys ask me questions then talk with Mrs. Selegan. [15 mins]
- Product pricing - introduction to product pricing strategies [infographic, video, and formula card, 25]
- Product pricing - using the cost based pricing formula or the other pricing strategies start calculating your product retail (sell) price and create a list of product prices. [15 mins]
Wednesday 31 August
- Do now starter activity - carry on with your price list [5 mins]
- Why business planning? Finding common understanding [Poll, 10 mins]
- Revise why business planning [infographic, 5 mins]
- Introduce business plan template [5 mins]
- Why plan objectives? Introduction to smart objectives [infographic, 15]
- Concluding activity and homework - write 2 SMART objectives for your market day plan [15 mins].
Resources
Two links below in addition to the attached resource files.
- Why a business plan [poll] - Go to this link https://pollev.com/shamsalchalabi195
- Competitive-based pricing video - watch
-
Kia ora class,
This week we continue our focus on business planning. Remember that the business plan template available on your Google Classroom is your assessment template and you need to work through it with me from now and commit to completing your tasks on Google Classroom every week.
First we are finalising our SMART objectives and you are expected to submit at least 3 of those into the corresponding activity on Google Classroom by the end of our Monday lesson.
We will then move to the very first step any business need to take when establishing its presence in the market, that is branding!
Mātauranga Māori
I would like to take the opportunity to unpack another Māori concept as we embark on this business planning journey.
"E tio te tūī , e ketekete te kākā, e korihi te kokako", it takes many instruments to make a symphony.
The whakatāuki below carries wisdom that we can apply to different aspects of our lives - socially, politically, and commercially. In a business context it is crucial that we plan and manage business tools and resources efficiently to thrive and succeed.
Learning Intentions/ Mo te ako
- Learn how to write business objectives using the SMART criteria.
- Understand branding principles through small business case studies.
Success Criteria
- Write at least 3 SMART goals for your business.
- Design a business brand kit including: Business name, logo, and brand colours.
Learning Sequence
Monday 5 September
- Continue writing SMART objectives and submit to Google Classroom [20 mins]
- Do logo quiz (will be hosted in class) and discussion of logos matter? [15 mins]
- Get starting at 'why brand matters pdf' [15 mins, may carry over to Wednesday]
Wednesday 7/9/22
- Continue from 'why brand matters pdf'
- Do brand personality test and discussion [25 mins]
- Discuss the small business branding case study pdf [25 mins]
-
Kia ora class,
This week we continue our focus on business planning. Remember that the business plan template available on your Google Classroom (under Business Planning topic) is your assessment template. You need to work through the template with me and commit to completing your tasks on Google Classroom every week right to the end of this term.
This week we finish the first step every business needs to take when establishing its presence in the market, that is branding and developing business vision and mission statements.
We will then move to the market research section of the business plan. However, since we have already covered most of it (under the Market Research topic on Google Classroom) we will focus on SWOT analysis.
Mātauranga Māori
I would like to take the opportunity to unpack another Māori concept as we embark on this business planning journey.
"E tio te tūī , e ketekete te kākā, e korihi te kokako", it takes many instruments to make a symphony.
The whakatāuki below carries wisdom that we can apply to different aspects of our lives - socially, politically, and commercially. In a business context it is crucial that we plan and manage business tools and resources efficiently to thrive and succeed.
Learning Intentions/ Mo te ako
- Identify and develop the main immediate purpose and the long term goal of your business.
- Identify business strengths and weaknesses, and anticipate opportunities and threats to your business.
Success Criteria
- Write a business mission (purpose) and vision (aim) statements (including a slogan where necessary).
Write a detailed SWOT analysis for your business presented as a grid or a graphic.
Learning Sequence
Monday 12 September
- If you haven't submitted your homework 'Branding Matters' you will need to do so at this beginning of this lesson [5 mins]
- Watch 'what is vision statement' [Video Link] and 'examples of vision statement' [Video Link] videos then each group to write a vision statement and submit to Google Classroom Task 'Write a Vision Statement' [20 mins].
- Watch the videos 'vision vs mission statements' [Video Link] and 'examples of mission statement' [Video Link] then each group to write a mission statement for their business and submit to Google Classroom Task 'Write a Mission Statement' [20 mins].
Wednesday 14 September- Presentation and discussion of the 'SWOT Analysis Explained' infographic.
- Using a step-by-step method you will work on writing a SWOT analysis for your business and submit it to the class task under business planning topic 'Write a SWOT analysis for your business'. on Google Classroom.
-
Kia ora class,
As we continue our focus on business planning, remember that the business plan template is available on your Google Classroom under (Business Planning) topic, and it is your assessment template. You need to work through the template with me and commit to completing your tasks on Google Classroom every week right to the end of this term.
This week we will finalise the following sections of the business plan:
- Market Research: 1) Finalise and submit your SWOT analysis. 2) Recap on market research methods and analysis.
- Marketing Mix: Recap on what we expect to see in your assessment in relation to your market day products.
- People: We will focus on understanding organisational structures, chart of group members, and roles and responsibilities [new learning material attached in the resources section below].
Learning Intentions/ Mo te ako
- Recap on previous learning of Market Research , Marketing Mix, and Product Costing.
- Locate human resource needs for a business by recognising different organisational structures.
Success Criteria
- Submit all required materials for market research to the Checkpoint 2 station on Google Classroom.
- Draw an organisational chart for your Market Day business , including description of roles and responsibilities.
Matauranga Māori
We continue to be guided by the whakatāuki below carries a wisdom that we can apply to different aspects of our lives - socially, politically, and commercially.
"E tio te tūī , e ketekete te kākā, e korihi te kokako", it takes many instruments to make a symphony.
For our learning focus this week on organisational structure, this Māori concept alerts us to the vital role people (employees) play in the success of any business. The analogy of the instruments playing together to make a symphony is closely connected to an essential part of any business practice: managing human resources. Because through proper allocation of roles and delegation of responsibilities, people work in harmony, similar to playing a symphony!
Learning Sequence
All activity instructions are on Google Classrooms
Monday 19 September 2022
- Finalise and submit SWOT analysis to the corresponding task on Google Classroom [10 mins].
- Recap on Market Research section (Business Plan Template), refer to 'Market Research' topic on Google Classroom [10 mins].
- Recap on Marketing Mix section (Business Plan Template), refer to 'Marketing Mix' topic on Google Classroom [15 mins].
- Recap on Finance section (Business Plan Template), refer to 'Product Pricing' activity under 'Business Planning' topic on Google Classroom.
Wednesday 21 September 2022
- Discussion with Mrs Selegan about Market Day product, finalising options.
-
Kia ora class,
As we continue our focus on business planning, remember that the business plan template is available on your Google Classroom under (Business Planning) topic, and it is your assessment template. You need to work through the template with me and commit to completing your tasks on Google Classroom every week right to the end of this term.
This week we will finalise the following sections of the business plan: People and Operations.
Learning Intentions/ Mo te ako
- Locate human resource needs for a business by recognising different organisational structures.
- Understand the health and safety requirements for small businesses.
Success Criteria
- Draw an organisational chart for your Market Day business , including description of roles and responsibilities.
- Write a 'Health and Safety' document for your staff to check and follow on Market Day.
Matauranga Māori
We continue to be guided by the whakatāuki below carries a wisdom that we can apply to different aspects of our lives - socially, politically, and commercially.
"E tio te tūī , e ketekete te kākā, e korihi te kokako", it takes many instruments to make a symphony.
For our learning focus this week on organisational structure, this Māori concept alerts us to the vital role people (employees) play in the success of any business. The analogy of the instruments playing together to make a symphony is closely connected to an essential part of any business practice: managing human resources. Because through proper allocation of roles and delegation of responsibilities, people work in harmony, similar to playing a symphony!
Learning Sequence
All activity instructions are on Google Classrooms
Monday 26 September 2022 (Public Holiday)
Wednesday 28 September 2022Today we focus on the 'People' and 'Operations' section of the Business Plan.
- Start by understanding the term 'organisational structure' [10 mins].
- Explore the different structures of a business through in class group activity [25 mins].
- Decide on a structure for your Market Day business and allocate roles by drawing a chart of your business structure that outlines members (employees) roles and responsibilities in the business [complete as a homework].
- Using the 'Roles and Responsibilities Chart' example, write a list of roles and responsibilities for each member (employee) [self directed task/homework].
- Checkpoint 2 on Google Classroom: Submit required documents [5 mins].
- Go through the health and safety sample document from Otago Farmers Market to guide you in creating one for your business [10 min].
- Write a 'Health & Safety' checklist for your staff to reduce potential risks on Market Day.
Tasks outlined above have to be submitted to the corresponding tasks on Google Classroom:
Task 1: Draw a Business Structure [class activity].
Task 2: Outline Roles & Responsibilities Within Your Business [homework].
Task 3: Write a 'Health & Safety' checklist for your staff to reduce potential risks on Market Day. -
Kia ora class,
As we continue our focus on business planning, remember that the business plan template is available on your Google Classroom under (Business Planning) topic, and it is your assessment template. You need to work through the template with me and commit to completing your tasks on Google Classroom every week right to the end of this term.
This week we will finalise the following sections of the business plan:
- Market Research: 1) Finalise and submit your SWOT analysis. 2) Recap on market research methods and analysis.
- Marketing Mix: Recap on what we expect to see in your assessment in relation to your market day products.
- People: We will focus on understanding organisational structures, chart of group members, and roles and responsibilities [new learning material attached in the resources section below].
Learning Intentions/ Mo te ako
- Recap on previous learning of Market Research , Marketing Mix, and Product Costing.
- Locate human resource needs for a business by recognising different organisational structures.
Success Criteria
- Submit all required materials for market research to the Checkpoint 2 station on Google Classroom.
- Draw an organisational chart for your Market Day business , including description of roles and responsibilities.
Activities:
- Business Studies Assessment 1 due- Friday Week 1
-
Kia Ora Everyone
Learning Intentions: We are learning to (WALT)...
Make our products in preparation for Market Day
Success Criteria: I can/have...
Using the P's of marketing I can apply these concepts this when producing my product
Activities:
1. Please follow the timeframe to the countdown to Market Day - Tuesday: 1 November 2022.
2.Follow the timeline on Google classroom
3. Use the checklist on google classroom to determine if you are ready or not.
-
Kia Ora Everyone
Learning Intentions: We are learning to (WALT)...
Reflect on Market Day
Success Criteria: I can/have...
Reflected on the market day process
Activities:
1. Market Day: 1 November 2022.
2. SaVy workshop- Basic financial literacy skills
-
Kia Ora Everyone
Learning Intentions: We are learning to (WALT)...
Reflect on Market Day
Success Criteria: I can/have...
Reflected on the market day process
Activities:
1. Please complete Market Day evaluation sheet
2. Discuss results from evaluation sheet
3. Les Mills Activity
-
Kia Ora Everyone
Learning Intentions: We are learning to (WALT)...
Find Solutions/ideas to a case study
Success Criteria: I can/have...
Developed positive partnerships by collaborating in my group
Used my critical thinking and literacy skills to understand and unpack the text/case study.
Activities:
1. Les Mills Activity - Refer to the google classroom page to complete this activity
2. Groups should be maximum to 4 students per group.
3. Read the case study in detail
4. Use mind maps to extract information from the case study.
5. Follow the guideline to present your findings work to the class.
6. The best idea/presentation wins a prize.
-
Kia Ora EveryoneLearning Intentions: We are learning to (WALT)...
Find Solutions/ideas to a case study
Success Criteria: I can/have...
Developed positive partnerships by collaborating in my group
Used my critical thinking and literacy skills to understand and unpack the text/case study.
Activities:
1. Les Mills Activity - Refer to the google classroom page to complete this activity
2. Groups should be maximum to 4 students per group.
3. Read the case study in detail
4. Use mind maps to extract information from the case study.
5. Follow the guideline to present your findings work to the class.
6. The best idea/presentation wins a prize.
-
Kia Ora EveryoneThis is final week to wrap up your slideshow. Next week each group will be presenting their final ideas
Learning Intentions: We are learning to (WALT)...
Find Solutions/ideas to a case study
Success Criteria: I can/have...
Developed positive partnerships by collaborating in my group
Used my critical thinking and literacy skills to understand and unpack the text/case study.
Activities:
1. Les Mills Activity - Refer to the google classroom page to complete this activity
2. Groups should be maximum to 4 students per group.
3. Read the case study in detail
4. Use mind maps to extract information from the case study.
5. Follow the guideline to present your findings work to the class.
6. The best idea/presentation wins a prize.
7. SaVy workshop- Wednesday- Financial literacy
-
Kia Ora EveryoneThis week you will be presenting your ideas in your groups
Learning Intentions: We are learning to (WALT)...
Find Solutions/ideas to a case study
Success Criteria: I can/have...
Developed positive partnerships by collaborating in my group
Used my critical thinking and literacy skills to understand and unpack the text/case study.
Activities:
1. CETA Quiz
2. Presenting your final ideas for your Case Study
-
Hope you enjoyed Business Studies this year.
Best wishes for the rest of the year, have a great festive season.
