10 Business Studies 3
Section outline
-

Tēnā koutou katoa e te whānau. Nau mai haere mai.
Welcome to Year 10 Business Studies 2022. I am Mr Keung or some of you may already know me as Matua Anthony. I hope that we will enjoy our journey together in exploring the business world and developing an enterprising mindset. You never know but the next Bill Gates, Elon Musk may be sitting in our classroom this year. I am in M6 this year. Feel free to come and chat or email me if there is anything that I can help you with. My door is always open for you.
Mauri ora!
CONTENTS- Team building
- Entrepreneurs
- Types of Business
- Markets & segmentation
- Market Research
- Marketing Mix - Product, Price, Place, Promotion
- NCEA 1.4 Marketing Mix
- The role of markets - houses, shares, commodities
- Economics
- Business Issues, goals and stakeholders
- Finance & Accounting
- Market Day - putting it all together
- Web text - Wikibooks GCSE Business Studies
-
Business & Our Lifestyles
For the first week we will get to know each other better (whakawhanaungatanga) as we prepare top work together in teams on various projects throughout the year. We will also look at the importance of business in our lives today
Success Criteria: I can.......
- recognise the importance of business activity in today's society
- identify the benefits and drawbacks of business activity
- recognise the importance of the skills of teamwork, communication and problem solving to business success
Activities:
- Team building & problem solving activities
- Decision making & communication games
-
Innovation & Creativity

Kia ora everyone
This week we will be focusing on creativity. We will also look at how enterprising people use the concept of creativity and innovation to enhance their business/projects/lives etc.
Learning Intentions
- recognise the characteristics of innovation
- to learn how to work in a team
- to apply our enterprising skills in different scenarios and challenges to achieve our goals.
- the need for businesses to seek advice to help start, run and develop their organisation.
Success Criteria: I can/have...- understand the importance of creativity & innovation to business success
You may complete these tasks in pairs.
Task 1
Watch the following video and write a definition for creativity and innovationTask 2: Innovations
Watch the video below "The 71 Most AMAZING Innovations of All Time." and then complete the questions listed below:
- List your own personal top 5 innovations from those mentioned in the video
- The video suggested that these innovations have resulted in people living longer, healthier and happier lives. Using a couple of these innovations as an example, explain how this innovation is so important to you or your lifestyle.
Task 3: History of Innovation Task
Choose an everyday product used at home or at school (e.g. pen, calculator, oven, washing machine, phone etc) and complete the following tasks on a slideshow (include pictures if possible):
- Invention: The first product of its kind. Include any relevant information, who created it, where, when, what it was made of etc. What is it? What does it do? What is it used for? Explain how it was useful and made life easier for people.
- Innovations: Show 2-3 innovations over time up until the latest product of its type today. For each of these innovations show and explain how each innovation was better, different or more useful than previous versions.
You will have this week to complete these tasks.
- recognise the characteristics of innovation
-
Innovation: What's next?
This week you will put your own creative and innovative skills into action by brainstorming and designing a new innovation to your chosen product.
Success Criteria: You will be able to;
- recognise and follow the principles of brainstorming
- understand the characteristics of innovation
- explain how your idea is innovative
Characteristics of Innovation
For something to be innovative in business it must:
- have something new about it. (design, feature, function, colour, size etc)
- be improved. It should offer something different or do something better than existing products
- have economic value. People must be willing to buy or pay for this innovation
Principles of Brainstorming
- Generate as many ideas as possible.
- Defer Judgment. Creative spaces are judgment-free zones—they let ideas flow so people can build from each other's great ideas.
- Encourage Wild Ideas
- Build on the Ideas of others
Activity:
In a group of 2-3 brainstorm an idea for a new innovation to your chosen product. You should create a presentation to sell this idea to some investors. You may draw a poster, create a slideshow. It's up to you. Be creative!
-
Achievement Objectives (Level 3&4 of Social Studies Curriculum)
- Understand how people make decisions about access to and use of resources
- Recognise the economic problem and the consequences for communities and societies
- Understand how exploration and innovation create opportunities and challenges for people, places, and environments.
- Understand how producers and consumers exercise their rights and meet their responsibilities.
- Understand how producers and households make decisions that impact on communities.
- Understand how people participate individually and collectively in response to community challenges.
Success Criteria
Students will be able to:
- Describe why business activity is needed.
- Recognise how business influences our lifestyles.
- Describe the economic problem in relation to the concept of scarcity and choice
- Define the following economic terms: households; producers; economic means (time, skills & money); needs & wants; opportunity cost; circular flow
What we have versus what we want
What we have: Our means
We all have time, skills & money. These are referred to as our means. We use our means to enjoy a certain lifestyle. Our means are limited.
What we need & want:
All people have needs and wants. Our basic needs are food, warmth and shelter. Without these things we would not be able to survive. Our needs & wants are unlimitedWe use our means (time, skills & money) to satisfy our needs and wants. Because our needs and wants are unlimited but our means are limited this means we must choose which needs and wants we wish to satisfy.
When we make a choice, we give up the opportunity of doing other options. Opportunity cost is the cost of not doing the second best next best option or alternative.
Tasks:
Complete the worksheet on google classroom
-
Welcome back to school. Hopefully you are feeling refreshed and ready to work. This term we will prepare for our first assessment. For some of you, this will be the NCEA Achievement Standard (AS90840) Apply the marketing mix to a new or existing product.
This week we will review the marketing mix and begin focusing on the first and most important "P" of the 4P's in the marketing mix, PRODUCT!
The 4P's: PRODUCT
Marketing is about focusing business activities on satisfying the needs and wants of customers. A businesses products or services are most important because it has been produced for that purpose. To be successful a business must ensure they have the right type of product that is in demand for their market. Most markets have many competitors so a business will try and offer something that is different or better than the competition. They often look to create unique selling points to their products or services that distinguish their products from the competition. This could include product modifications or innovations (new features) to products or services. This can also be achieved through packaging and branding. In business, when it comes to developing a product, the design, quality, packaging, features, and functions should all be considered. -
Product
Product is the most important “P” in the marketing mix. A successful product has to fulfil a specific need in the market. It’s design, appearance, packaging are all important factors. Functionally, it must be able to perform its function as promised.
In applying marketing principles, businesses should develop and design their products with their target market in mind. The design, appearance, colour and size of a product should appeal to the target market.
The purpose for why consumers would use the product would also be considered in the development of the product. Product Functions, or the things that product is able do, should also be designed to meet the needs of the target market.

For example, this vacuum cleaner has been designed for commercial use. The target market is professional cleaners who need a vacuum cleaner that is powerful, portable or easy to move around. The design of this vacuum includes a backpack so users can move freely around rooms without the vacuum getting caught on furniture etc. It has a powerful 1000W motor that allows rooms to be cleaned better and faster. All of these functions were considered during the design and development phase of the product.
Task:
Choose a specific product to profile and then complete the following tasks on a doc or slideshow:
Product description.
Fully describe your chosen product. Your description should include:
- Name of the product
- Name of the company that makes or sells this product?
- Features of your product. Colour? Size? Specs etc.
- Functions of the product. What does it do? OR what is it used for?
- Why do people buy your product? What needs or wants does it attempt to satisfy for consumers?
- Include a picture of your product.
Target Market description
- Describe the intended target market of this product. Ensure that you look at a range of factors (at least three) from demographic, psychographic, lifestyle etc. in your description.
- Explain or give reasons for your choices. Use examples from any features or functions of the product that will appeal to your specified target market. Explain how these features or functions help to satisfy the needs of your target market.
-
Product Packaging
DO NOW! Watch the video below then write a short summary to explain "why boxes are most commonly used as packaging for products?"
Packaging can often as important as the product itself. The most important function of packaging is to minimize product damage. However, packaging can be used for so many more marketing purposes that some marketing experts consider it be the '5th P' of the marketing mix. Packaging can be seen as an opportunity to shows off the product. It can be used to display the price and value of the product and it is a way to communicate the product’s benefits to consumers.
Some other functions of packaging:
Packaging can:
- add to a products usefulness. E.g. Drinks with straws, easy pour spout
- contain and preserve the product
- facilitate the filling of the package
- make the product easy to close or open
- allow the product to be packed and carried easily
- allow the product to be durable for distribution
- attract attention on the shelf
- can be used as a vehicle for segmentation. E.g. For people who live alone, products like Soup in a cup, or Sara Lee’s single serve cake. OR Family packs, OR packaging for bulk or commercial use.
- be used for branding and labelling purposes
- add visual appeal to draw attention of customers
Task:
Describe the features of the packaging used for your chosen product. Look at the functions of packaging (from above notes OR on slideshow on google classroom) and see if any apply to your product.
Fully explain (give reasons) the purpose of the packaging features used for your product.
-
Unique Selling Points (USP's)
An important part of the marketing of the product is through product differentiation. This means making the product different from its competitors. These differences are often referred to as unique selling points
This can be achieved through:
- Distinctive design– e.g. Dyson; Apple iPhone
- Packaging – e.g. Toblerone
- Performance - e.g. Mercedes, BMW
- Branding - e.g. Nike, Reebok
Branding
Branding is one method that businesses use to make their products or services unique or to stand out from the competition. It may include:
- brand image
- unique name or logo
- unique packaging
- unique functions:
Brand creates & influences consumers perceptions of the business or their products & services. Branding is about creating an image that a business wants people to think about their company and products. Business may spend a lot of money on promoting their brand image. Some businesses spend very little.
Task: Branding & Consumer Perceptions
.
- What are your perceptions of these two brands?
- Describe the target market that these brands would appeal to.
- Explain why these perceptions might appeal to the intended target market.
- How much do you think each business use to promote its brand image? Explain.
-
Product Life Cycle
Products do not last forever. Like people, they go through different stages in their life. The life cycle of a product is broken into four stages—introduction, growth, maturity, and decline although some marketers also include a "saturation" stage between maturity & decline.
It is often used by marketing experts as a planning tool in deciding when it is appropriate to increase advertising, reduce prices, expand to new markets, or redesign packaging. This tool has a some limitations as not all products follow a smooth and predictable growth path.
Task 1: Stages of the PLC
What stage of the PLC would the following products be in?
- PS4
- Iphone 6
- Samsung Galaxy Z Fold
- Watties baked beans
Task 2: Informative v Persuasive Advertising & PLC
Watch the two advertisements above and then answer the following questions:
- What information is given about the Iphone 12 in the first advertisement?
- Explain why the Iphone advertisement contains more information than the Nike ad.
- What stage of the PLC is the Iphone 12 in? Explain why this type of advertising would be appropriate given the stage of the PLC that it is currently in.
- What information is given about a NIKE product in the second advertisement?
- What is the message of the Nike ad? What perceptions (ideas or thoughts) does the ad try to portray about people who use Nike products?
- Why is this type of advertising suitable for this stage of the PLC for Nike products.
-
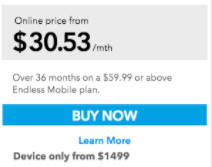
Price
Determining the price of a product is an extremely important decision because it determines the amount of profit a business will earn from sales of their product.
Factors to consider:
- Costs of production: The price that the business charges must recover the costs of production in order to make a profit.
- Competitive conditions in the market: Demand and supply in the market needs to be considered. If demand for a product is high but supply is low, then a business can take advantage of the market conditions and charge a higher price in order to maximise profits. For example, petrol & oil. When supply in the market is low, petrol companies raise their prices.
- Competitors prices: The business will need to ensure that the price charged is reasonable compared to competitors products or they may lose sales to the competition.
- Stage of the product life cycle: The age of the product may have an effect on the price of a product. For some products like grocery items their price remains relatively constant unless market conditions change or the business runs some promotions etc. Other products (like technology), the price may lower over time due to newer, more advanced models entering the market.
- Price/Quality perceptions: It is also important as the chosen price may also create perceptions to consumers about the quality of the product. Consumers naturally perceive that high-priced products are also of a high quality and vice-versa. Thus, when choosing a price for its product, a business must be careful to choose a price that will fit the rest of the marketing mix and most importantly will appeal to its target market. The chosen price should complement the chosen brand image for the product.
- Pricing strategies for new products vs. existing products: For new products entering a competitive market some businesses may decide to charge a price lower than the competition to try and entice consumers who buy existing brands to possibly try their product and like it so that later in the products life cycle (as they gain regular customers) they may then increase their price. This is called a price penetration strategy.
Pricing Strategies
Cost-Plus Pricing
The business takes into account the cost of manufacturing the product and then adds on a profit mark-up. This can either simply cover costs or include an element of profit. It focuses on the product itself and does not take into account consumers’ expectations or perceptions. It is very easy to apply but the business may lose sales if their price is more than competitors.
Penetration Pricing
This is where the business sets the price lower than the competition to ‘penetrate the market.’ This is often useful when launching into a new or highly competitive market. It is typically used with mass market products – chocolate bars, food stuffs, household goods, etc. It is also suitable for products with long anticipated product life cycles.
Other benefits:
- Market share is quickly won.
- Encourages consumers to develop a habit of buying
- ‘Low’ price to secure high volumes
Price Skimming Strategy
This is where the business sets an initial high price for a unique product encouraging those who want to be ‘first to buy’ to pay a premium price. Later in the products life cycle they may then lower the price. It is usually used alongside a promotional campaign to create high demand for the new product before it is even launched. This strategy helps a business to gain maximum revenue before a competitor's product reaches the market. This is often used with technology products like mobile phones and devices.
Loss Leaders
This is where chosen goods/services are deliberately sold below cost to encourage sales elsewhere in the business. The business hopes that the purchases of other items more than covers ‘loss’ on item sold. It is typically used in supermarkets, e.g. at Christmas, selling bottles of coke at $0.99 in the hope that people will be attracted to the store and buy other products as well that will cover the loss made on the coke. Cell phones & contracts are another example.
Psychological Pricing.
This when particular attention is paid to the effect that the price of a product will have upon the consumers perceptions of the product. It may involve charging a very high price for a high quality product so that high income customers may wish to purchase it as a status symbol. E.g. Ferrari. Alternatively, it may charge a more reasonable or lower price so that consumers perceive it as an ‘affordable’, ‘value for money’ product.
 Another example of psychological pricing is selling products for $199 instead of $200 is also an example of psychological pricing as it creates the impression of being much cheaper.
Another example of psychological pricing is selling products for $199 instead of $200 is also an example of psychological pricing as it creates the impression of being much cheaper.Promotional Pricing
This is when products might be sold “on sale” or at a lower price for a short period of time. It includes “buy 1 and get 1 free” deals. It is useful for getting rid of unwanted stock. It could help renew interest in a business if sales are falling. The challenge for businesses is that the lower price also reduces sales revenue and profits.
-
Promotion
The aim of promotion is to:
- increase awareness
- create interest
- provide information
- stimulate demand to generate sales
- differentiate the product or create brand loyalty
- Reinforce the brand
Promotional Strategies
A business will plan and implement a promotional strategy to inform their intended target market of the product or service. The strategy may include methods like advertising, sales promotions, sponsorships, public relations campaigns, point-of-sales displays etc. They may use a wide variety of media from TV, radio, social media, newspapers, magazines etc.

Task: Research at least two of the methods above that your business uses to promote its brand or products. For each method:
- Describe how the method is used.
- What are the benefits of using this promotional method? What are the costs or drawbacks?
- Find examples of how your business uses these methods and describe them.
- Who is this promotion aimed at? Who is the intended audience?
- What is the intended purpose of this promotional activity for the business (increase awareness, create interest, provide information etc.)?
- In your opinion, is the promotional method used effective? Explain why or why not. Justify your answers
-
Learning Intentions
- To apply what we've learned in class to a real life product
- To experience an NCEA Level 1 assessment (and hopefully gain 3 credits at Excellence)
- Have decided which product's marketing mix to analyse and have planned, and completed, research.
- Have completed part of the final report
NCEA 1.4
NCEA AS90840 (1.4) Apply the marketing mix to a new or existing productLOOK at these examples of student work as90840 and read the examiner's comments.
http://www.nzqa.govt.nz/ncea/subjects/business-studies/annotated-exemplars-2/level-1-as90840/
Learning Intentions- To apply what we've learned in class to a real life product
- To experience an NCEA Level 1 assessment (and hopefully gain 3 credits at Excellence)
- Have read the student instructions again and the examples of student work with examiner comments
- Have completed the final report
Assessment is due Friday 6 August (Week 2) at 4:00pm.
-
Place
Place refers to the distribution methods and location businesses use for their products or services to be easily accessible to the target customers. It is how the product is bought and where it is bought.
Business location is a unique factor that can give a business strong competitive advantage.
- Factors to consider:
- Costs of lease/owning store
- Customer Traffic − Number of customers visiting the location etc
- Convenience − Proximity to residential areas, proximity to public transport facility.
Task 1: What affects place decisions?
- Read each of the factors from the link below
- Identify and describe which factors apply to your chosen product. Type of product? Technicality? Purchase frequency? Price? Durability? Location of customers? Where do competitors sell their products?
https://igcseaid.com/notes/business-studies-0450/3-3-marketing-mix/
Distribution Channels
A business may decide to sell their products directly to its customers or may use resellers like wholesalers and retailers to sell their products. The factors that you looked at in Task 1 above will be considered in making thiese decisions.
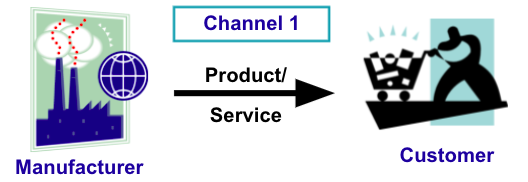
Direct Selling
The product is sold to the consumer straight from the manufacturer. Distribution methods may include, but are not limited to, door-to-door, retail, online sales, mail order.
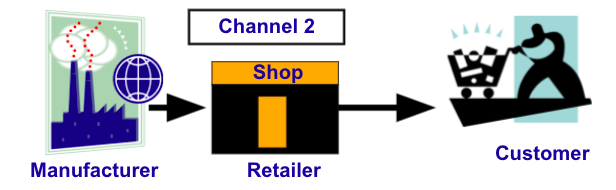
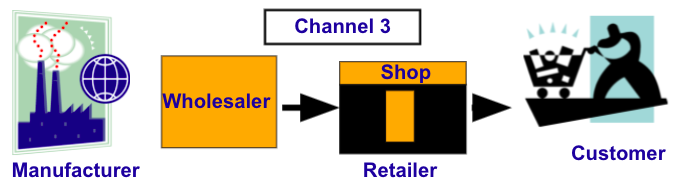
Using Resellers
Manufacturers can choose to sell products directly through wholesalers or retailers or vendors as a distribution strategy. There are a number of distribution channels available:
Sometime when a manufacturer sells in overseas markets they may also use an agent who has expertise in the overseas market to distribute their products. This is sometimes referred to as a channel 4 distribution channel
CHANNEL 4
MANUFACTURER ------AGENT------WHOLESALER--------RETAILER------CONSUMER
Task 2: Distribution Channels
- Identify which channel of distribution the manufacturer of your business uses?
- Identify which channel of distribution competitors use?
- Go to the link below and look at the table of the advantages and disadvantages for each channel of distribution. Using the channel of distribution you identified in Q1. List the advantages and disadvantages for the business of your chosen product.
OTHER DISTRIBUTION STRATEGIES
Selective Distribution Strategy
This strategy is where a business may choose to distribute products only to a few select businesses or customers in a specific geographical area. It is often used for selling upscale products and is sold by resellers who deal only with high-quality products.
Benefits
The business is able to ensure that the selected outlets meet the image of the brand to ensure customers have a good experience. Improved customer satisfaction will lead to repeat purchases and customer loyalty.
Exclusive Distribution Strategy
This strategy restricts product distribution to only one reseller in a geographical area. The reseller will have exclusive rights to sell the product or service. Often used with specialty products that you can promote as prestigious because you are the sole supplier and the intermediary is the sole reseller.
Exclusive distribution is an agreement between a distributor and a manufacturer that the manufacturer will not sell the product to anyone else and will sell it only to the exclusive distributor. At the same time, even the exclusive distributor has to enter the agreement that he will only sell the products of the manufacturers exclusively and will not sell those of the competition. This ways, the market is an open ground for the manufacturer and the distributor and they have complete control on the distribution of the product.

-
Assessment 2 information

Assessment 2 is to be confirmed, but will be based on your work towards Market Day.
You'll produce a group Business Plan for your Market Day business and product. The deadline for submitting the Plan will be announced soon (likely to be late this term).Market Day
Market Day is Term 4 Week 3 Tuesday (1st November) from 1:15pm to 1:50pm. Food items are allowed.
Rules:
- No on-selling existing products (eg Sprite) - make products from raw materials.
- Year 10s must have original, creative and high quality ideas & products.
- A product is
- a good (food, artwork, craft, food, soap, plants, etc) or
- a service (wash, paint, advertise, organise, etc) - No cooking at school. No entering the Food Tech room.
- Maximum of 4 group members
- There may be a fee paid by each group, which will be paid to charity
- Business Plan MUST include Health & Safety procedures, especially with food (photo evidence they were followed is needed).
- Promotion & Advertising on TV / poster permission from Whanau Dean or DP.
- On Market Day, remove all signs; don't leave 'bike shed' until teacher OKs it.
Simon Sinek's Golden Circle idea will help you be successful
https://www.ted.com/talks/simon_sinek_how_great_leaders_inspire_action?language=en
Here's a Business Plan template that might help
https://www.business.govt.nz/getting-started/business-planning-tools-and-tips/how-to-write-a-business-plan/ -
The 6 sections of the Business Plan are:
Introduction
(business description and key points from the business plan eg aim or purpose, specific SMART goals, timeline)Market research
(methods, findings, SWOT analysisMarketing
(marketing mix - Price, Product, Place, Promotion)People
(organisation chart of members & roles, responsibilities)Finance
(budgets & graphs explained, sources of finance, sales forecasts, costs & revenue)Operations
(running of the business (eg production, cash), quality control, health & safety procedures) -
Learning Process for 'Market Day'
We'll use the MHJC Learning Process to guide us towards Market Day.
Lost
We've started by identifying that there's a challenge that we're facing - to design, make, market and sell a product.


Explore
In your small group, brainstorm 100 words relating to ideas for products. Do NOT discuss the words. In particular, do NOT ridicule anyone for strange, left-field ideas, as it's these ideas that can lead to original, innovative products that other teams have not thought of.
Focus
Group your brainstormed words into 2 or 3 general areas (eg brownies, cakes and muffins could be grouped under sweet baking).
When you have 2 or 3 broad possible areas, do research online and think of skills and knowledge that you can access (team members or their family and friends) that might lend themselves to one of the ideas.
Choose one product / area to focus on.Starting a business
Resources
- Xero process:
https://www.xero.com/nz/resources/small-business-guides/how-to- Shopify - starting a business:
https://www.shopify.co.nz/guides/new-zealand/business-structures -
New deadline - Term 4 Week 1 Friday 4pm :)