25 July - 31 July
Section outline
-
Term 3 Week 1
Wecome back Y7M2. Hope you had a great term break.
Learning intentions for week 1.
We are learning to:
- connect number patterns and use tables, graphs, and diagrams to find relationships between successive number. L3.
- Use graphs, tables, and rules to describe linear relationships found in number L4.
- relate tables, graphs, and equations to linear relationships found in number. L5.
- relate rate of change to the gradient of a graph. L6.
Revisit last term's work by Mr. Hishey by completing Kahoot and Mathsbuddy question bank.
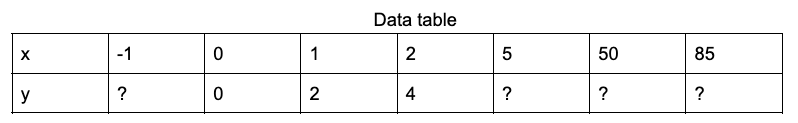
Q1. a) Look for a pattern in the number sequence.
b) Then complete the data table.
c) Plot the coordinates on a graph paper using x, y axis and joint the coordinates with a straignt line
d) Calculate the unit rate= Draw a straight line from x=1 up to the gradient. This standing line is called the Rise. Draw this on the graph. Use the y axis to measure this standing line. Now divide the rise with the measure of x which is x=1. (sleeping line or Run). The answer you get is called the unit rate.eg. One apple costs 2 dollars. That cost (y axis) of one apple (x axis) is called the unit rate. When you know the cost of one then you can calculate the cost of many. So, m is the cost of 1. times x is the cost of many. and y is the total cost, any added cost is c. So, Y = m times x+c.
e) When x= 0, y = 0. What is this corodinate point called? Y has been given a special letter here, what letter is it and what does it stand for?
f) From your graph create a rule for y =m time x +c.
g) Use your rule to solve, when f(x) = 85, y =?
h) confirm the graph is correct using your rule for y=mx+c.
i) Identify the idependent/dependent variables? explain.
j) Is the gradient positive/negative? Why? explain.
k) Explain c in y=mx+c. Why is c important?
Tue: Complete Q1 upto d).
Wed: Complete from e) to g).
Fri: Complete h) to k). Done!
