26 June - 2 July
Section outline
-
EXPLORE / TŪHURA learning intentions:
- We are EXPLORING ecosystems and the impact of climate change on the world's ecosystems.
- We are EXPLORING the ecosystems of New Zealand and the impact of climate change on New Zealand.
Climate Change - Ecosystems
Lesson Aim: TBAT identify the causes of climate change and explain the impact on a range of different global ecosystems.
Key Terms – what do these mean? (add them to your Global Book)
Climate change
Ecosystem
The Greenhouse Effect
The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect
Interdependence
Biodiversity
Sustainabilty
Greenhouse Effect vs Enhanced Greenhouse Effect
Explain the difference between the two different effects.What is causing climate change?
Volcanoes
Human causes:
Burning fossil fuels
Electricity generation
Vehicles
Deforestation
Agriculture
Rubbish
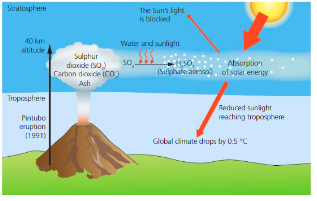
Volcanoes – CO2
Emit 1.5million metric tonnes of CO2 every day (2% of human emissions)
1991 Mount Pinatubo, Philippines
Cooled the climate by 0.5°C
Can heat – traps heat in
Volcanoes are a physical cause of climate change – either cooling or heating the earth, but they are not producing anywhere near the same quantities of CO2 as humans are.
- Burning Fossil Fuels
50% of all human induced greenhouse gases
Factories, cars etc
Carbon Dioxide is released as coal, oil and gas are burnt
Adds layers to the atmosphere – thickening it and trapping heat
20% of all human made greenhouse gas emissions
Cows produce the most of any other animal
Rice paddies
Flooding the fields creates anaerobic conditions which leads to methane production when decomposing
Anaerobic conditions = when the removal of oxygen is greater than it’s production. Less oxygen present means methane producing bacteria
Impacts of Climate Change
Temperature rising
Sea levels rise
Extreme weather
Loss of biodiversity
Changes to agricultural yields
What is an Ecosystem?
“a biological community of interacting organisms and their physical environment.”
Some different types:
Tundra/Polar
Tropical Rainforest
Savanna
Desert (hot and cold)
Temperate
Aquatic – freshwater and saltwater
Abiotic = not living: rock, soil, water and energy
Biotic = living (even when dead): vegetation and animals
Ecosystems
Task: Describe the location of one of the global ecosystems. (GSE)
G - Generally
S - Specifically
E - Exception
Challenge: Can you explain it’s location?Model Answers
ask – same format for any of the ecosystems. Say where they are generally, then add some continent/parts of continent or country specifics and then an exception if there is one.
Tropical RainforestGenerally the tropical rainforest is located close to the Equator.
Specifically in the continents of South America, Africa and South-East Asia. In South America tropical rainforest is located in the North East, mainly in Brazil.
An exception is that there is some tropical rainforest a bit further north in Asia, close to China.
Challenge
I think the tropical rainforest is located close to the equator because this is where there is band of low pressure. The low pressure is there because this is where the suns rays are most concentrated and it warms up the land. The land then warms the air above it and this means the air becomes less dense. The air rises and cools as it ascends into the atmosphere, eventually condensing to form water droplets and then clouds and raining. It is also so warm here because there is less atmosphere for the Suns rays to travel through, resulting in less reflection and more heat getting through to warm the area.
Desert
Generally – between the Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn (by the equator is not enough as this is where the rainforests are)
Specifically – northern Africa, West coast of S. America, central Australia, Central Asia
Exception – west coast of America (just north of the Tropic of Cancer)
I think the desert is located between the Tropics because this is where there is a band of high pressure where the Hadley and Ferrell cells meet. This means that the air does not rise and therefore very little rainfall occurs, resulting in dry/arid conditions of a desert.
Tundra
Generally – northern hemisphere/north/Arctic circle (map doesn’t show, but it would also be in the south in Antarctica)
Specifically – Northern Canada, Northern Russia, Greenland, Iceland
Exception – none
I think the tundra ecosystem is located at a high latitude in the north because this is where the Earth is coldest. Tundra is cold and dry. It is so cold here because the Suns rays have to pass through more atmosphere to reach the land and there is more reflection of the radiation back into space. There is also lots of snow here and this is a very reflective land surface and this means even more heat is reflected off and back to space. It is also very dry here because it is at a high pressure band, which means air is not rising and clouds do not form.
Ecosystem Processes
Interdependence
Everything is connected
Everything has a role to play to keep the ecosystem going
Examples of interdependence – the tree provides a habitat/shelter for the animal and the animal helps to spread the seeds on their fur or by eating and then getting rid. Trees and plants absorb the sunlight and photosynthesise, becoming producers in the food chain, consumers eat them and energy passes on, so on and so on until the ultimate predator. The predator dies and then fungi and other decomposers break the body down and it goes into the soil, nutrients are created (Carbon cycle) and vegetation grows again.
Research Task
Choose an ecosystem to research - Ecosystems: tropical rainforests, savanna, tundra, desert (hot/cold/both), temperate forests, coral reefs, etc
Research at least 5 types of vegetation and 5 types of animals that live here
Research how they link together e.g. birds and bats help to pollinate the flowers in a tropical rainforest
Research why this ecosystem is so important
Research how climate change is/will affect this ecosystem – try to find some information on how the vegetation and animals are/will be affected and what some of those impacts are (e.g increased temperatures are causing sea ice to melt in the Arctic which means the Polar Bears have no platforms to hunt from, resulting in them travelling into human settlements in Canada searching for food.)
Research any specific incidents that have occurred (e.g. bush fires in Australia 2020)
Research other human threats on the ecosystem e.g. palm oil plantations in the Indonesian Tropical Rainforest
Research some solutions to these threats e.g. individual and governmental changes
Present this information as:
A leaflet
Useful websites.
https://www.rainforest-alliance.org/articles/the-coolest-how-forests-affect-climate-change
https://wwf.panda.org/knowledge_hub/where_we_work/amazon/amazon_threats/climate_change_amazon/
Deserts
https://www.environmentalscience.org/deserts-ecosystems
https://www.britannica.com/science/desert
Coral reefs
https://www.noaa.gov/education/resource-collections/marine-life/coral-reef-ecosystems
https://www.un.org/en/chronicle/article/impacts-climate-change-coral-reefs-and-marine-environment
